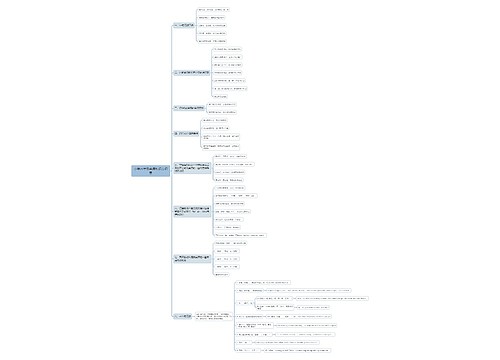
人教一起点英语六年级下册思维导图
U341947865
2024-12-30

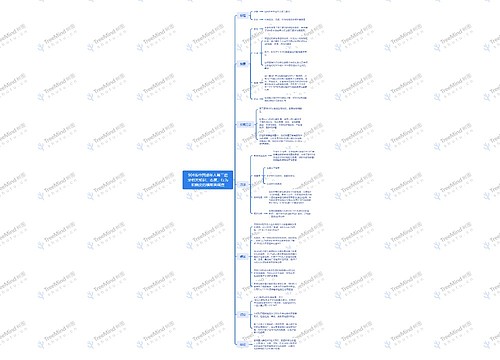
英语六年级教学内容重点讲解
树图思维导图提供《人教一起点英语六年级下册》在线思维导图免费制作,点击“编辑”按钮,可对《人教一起点英语六年级下册》进行在线思维导图编辑,本思维导图属于思维导图模板主题,文件编号是:3684536be07a95de9b4f98dfb9be17cc
思维导图大纲
相关思维导图模版
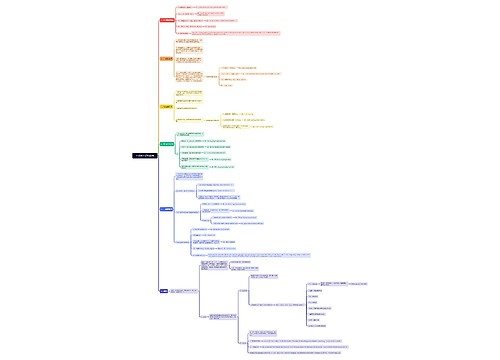
一、研究内容思维导图
 U682687144
U682687144树图思维导图提供《一、研究内容》在线思维导图免费制作,点击“编辑”按钮,可对《一、研究内容》进行在线思维导图编辑,本思维导图属于思维导图模板主题,文件编号是:4f21797dd3e8b08f1951dfc24e7be94f
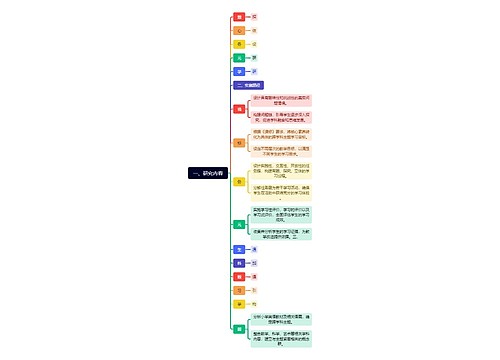
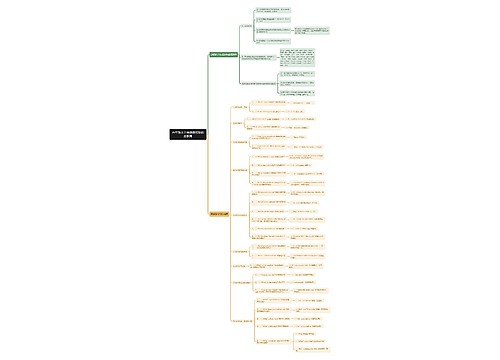
904名中国成年人第三磨牙相关知识、态度、行为和病史的横断面调查思维导图
 U633687664
U633687664树图思维导图提供《904名中国成年人第三磨牙相关知识、态度、行为和病史的横断面调查》在线思维导图免费制作,点击“编辑”按钮,可对《904名中国成年人第三磨牙相关知识、态度、行为和病史的横断面调查》进行在线思维导图编辑,本思维导图属于思维导图模板主题,文件编号是:10b9a8a2dd2fb4593f8130ef16c320fc