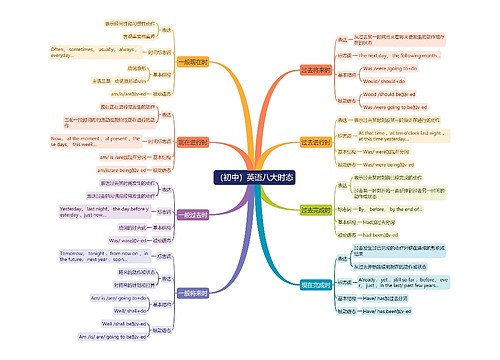
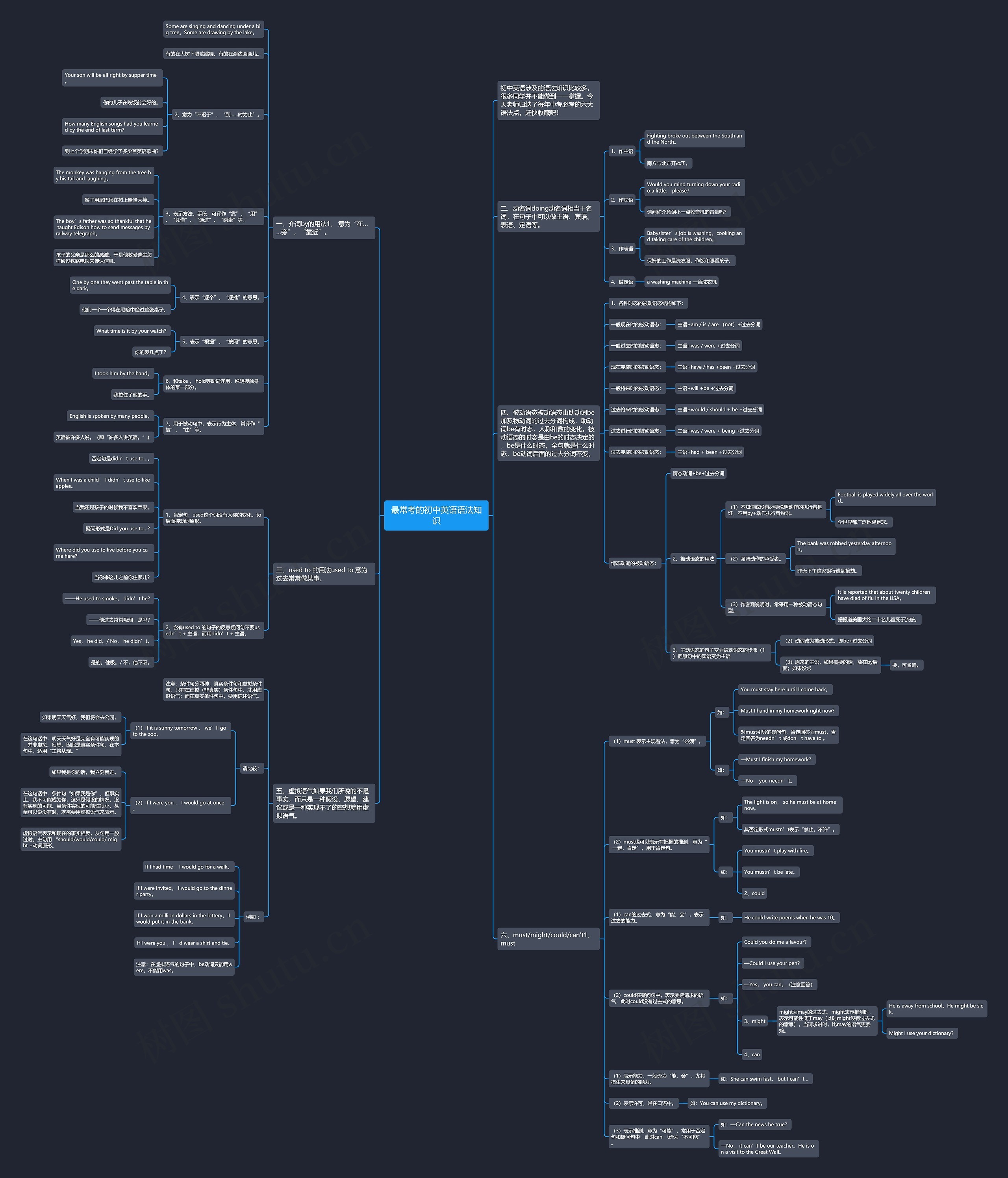
初中英语涉及的语法知识比较多,很多同学并不能做到一一掌握。今天老师归纳了每年中考必考的六大语法点,赶快收藏吧!
一、介词by的用法1、 意为“在……旁”,“靠近”。
Some are singing and dancing under a big tree。Some are drawing by the lake。
2、意为“不迟于”,“到……时为止”。
Your son will be all right by supper time。
How many English songs had you learned by the end of last term?
3、表示方法、手段,可译作“靠”、“用”、“凭借”、“通过”、“乘坐”等。
The monkey was hanging from the tree by his tail and laughing。
The boy’s father was so thankful that he taught Edison how to send messages by railway telegraph。
孩子的父亲是那么的感激,于是他教爱迪生怎样通过铁路电报来传达信息。
4、表示“逐个”,“逐批”的意思。
One by one they went past the table in the dark。
5、表示“根据”,“按照”的意思。
What time is it by your watch?
6、和take , hold等动词连用,说明接触身体的某一部分。
7、用于被动句中,表示行为主体,常译作“被”、“由”等。
English is spoken by many people。
二、动名词doing动名词相当于名词,在句子中可以做主语、宾语、表语、定语等。
1、作主语
Fighting broke out between the South and the North。
2、作宾语
Would you mind turning down your radio a little, please?
3、作表语
Babysister’s job is washing,cooking and taking care of the children。
三、used to 的用法used to 意为过去常常做某事。
1、肯定句:used这个词没有人称的变化,to后面接动词原形。
When I was a child, I didn’t use to like apples。
Where did you use to live before you came here?
2、含有used to 的句子的反意疑问句不要usedn’t + 主语,而用didn’t + 主语。
——He used to smoke, didn’t he?
Yes, he did。/ No, he didn’t。
四、被动语态被动语态由助动词be加及物动词的过去分词构成,助动词be有时态,人称和数的变化。被动语态的时态是由be的时态决定的,be是什么时态,全句就是什么时态,be动词后面的过去分词不变。
一般现在时的被动语态:
主语+am / is / are (not)+过去分词
现在完成时的被动语态:
主语+have / has +been +过去分词
过去将来时的被动语态:
主语+would / should + be +过去分词
过去进行时的被动语态:
主语+was / were + being +过去分词
情态动词的被动语态:
2、被动语态的用法
(1)不知道或没有必要说明动作的执行者是谁,不用by+动作执行者短语。
Football is played widely all over the world。
(2)强调动作的承受者。
The bank was robbed yesterday afternoon。
(3)作客观说明时,常采用一种被动语态句型。
It is reported that about twenty children have died of flu in the USA。
3、主动语态的句子变为被动语态的步骤(1)把原句中的宾语变为主语
(3)原来的主语,如果需要的话,放在by后面;如果没必
五、虚拟语气如果我们所说的不是事实,而只是一种假设、愿望、建议或是一种实现不了的空想就用虚拟语气。
注意:条件句分两种,真实条件句和虚拟条件句。只有在虚拟(非真实)条件句中,才用虚拟语气;而在真实条件句中,要用陈述语气。
请比较:
(1)If it is sunny tomorrow , we’ll go to the zoo。
在这句话中,明天天气好是完全有可能实现的,并非虚拟、幻想,因此是真实条件句,在本句中,适用“主将从现。”
(2)If I were you , I would go at once。
在这句话中,条件句“如果我是你”,但事实上,我不可能成为你,这只是假设的情况,没有实现的可能。当条件实现的可能性很小,甚至可以说没有时,就需要用虚拟语气来表示。
虚拟语气表示和现在的事实相反,从句用一般过时,主句用 “should/would/could/ might +动词原形。
例如 :
If I had time, I would go for a walk。
If I were invited, I would go to the dinner party。
If I won a million dollars in the lottery, I would put it in the bank。
If I were you , I’d wear a shirt and tie。
注意:在虚拟语气的句子中,be动词只能用were,不能用was。
六、must/might/could/can't1、must
(1)must 表示主观看法,意为“必须”。
如:
You must stay here until I come back。
Must I hand in my homework right now?
对must引导的疑问句,肯定回答为must,否定回答为needn’t 或don’t have to 。
如:
—Must I finish my homework?
(2)must也可以表示有把握的推测,意为“ 一定,肯定”,用于肯定句。
如:
The light is on, so he must be at home now。
如:
You mustn’t play with fire。
(1)can的过去式,意为“能、会”,表示过去的能力。
如:
He could write poems when he was 10。
(2)could在疑问句中,表示委婉请求的语气,此时could没有过去式的意思。
如:
Could you do me a favour?
3、might
might为may的过去式。might表示推测时,表示可能性低于may(此时might没有过去式的意思),当请求讲时,比may的语气更委婉。
He is away from school。He might be sick。
Might I use your dictionary?
(1)表示能力,一般译为“能、会”,尤其指生来具备的能力。
如:She can swim fast, but I can’t 。
(2)表示许可,常在口语中。
如:You can use my dictionary。
(3)表示推测,意为“可能”,常用于否定句和疑问句中,此时can’t译为“不可能”。
—No, it can’t be our teacher。He is on a visit to the Great Wall。
 U633687664
U633687664
 U582679646
U582679646