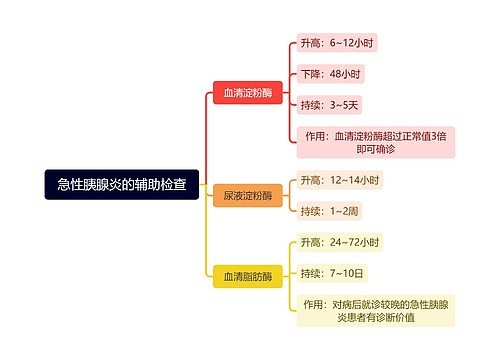
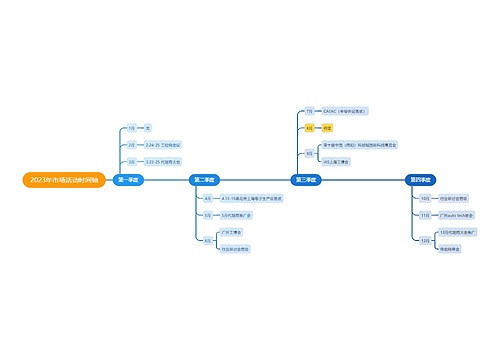
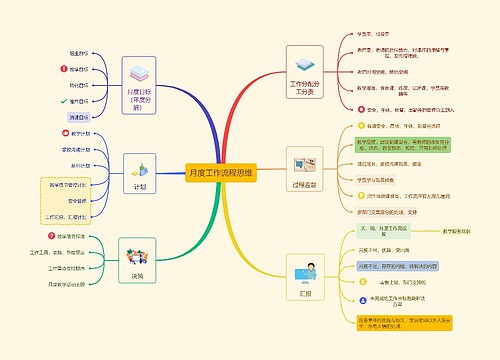
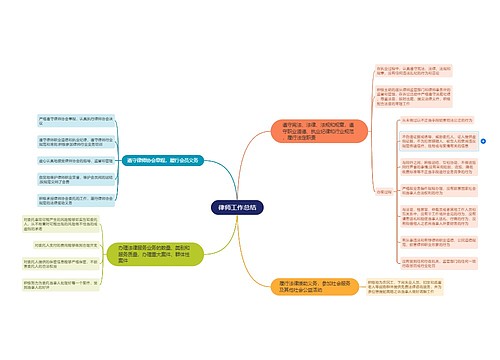
Classical music is a broad term, which usually refers to the mainstream music produced or rooted in the western etiquette and secular music tradition. From the 9th century to the present, the core norms of this tradition were codified between and. This period is called the period of common practice.
European music is different from many other non European and popular music forms to a great extent through its notation . From the beginning of the 20th century, Western staff notation has been used by composers to regulate the pitch, speed, beat, personal rhythm and accurate performance of music for performers. This has left less space for improvisation and improvisation This kind of music is often heard in European Art Music (comparing Indian classical music with Japanese traditional music) and pop music.
In particular, at the end of the s, public interest in and appreciation of such formal music declined in the United States and the United Kingdom. In this period, classical music lagged far behind the great commercial success of pop music. In some people's opinion, although the sales of CDs did not represent the popularity of classical music, the word _classical music_ did not appear until the beginning of the century, trying to change the concept of _classical music_ from John Sebastian _Classical music_ included in Oxford English Dictionary comes from about many writers who think that _classical_ is an inappropriate term to describe the mainstream and avant-garde music created since the second half of the century.
Therefore, threatening quotations are often used.
中文翻译:
古典音乐是一个宽泛的术语,通常指的是产生于或根植于西方礼仪和世俗音乐传统中的主流音乐,大约从9世纪到现在,这一传统的核心规范在和之间被编入法典,这一时期被称为共同实践时期。欧洲音乐通过其谱线符号系统,在很大程度上区别于许多其他非欧洲和流行的音乐形式,大约从世纪开始,西方的五线谱法就被作曲家用来给演奏者规定乐曲的音高、速度、节拍、个人节奏和准确的演奏,这就为即兴创作和即兴装饰等练习留下了较少的空间,在非欧洲艺术音乐(比较印度古典音乐和日本传统音乐)和流行音乐中经常听到这种音乐。特别是在世纪年代末,和英国,公众对这类正式音乐的兴趣和欣赏程度下降了,这一时期的古典音乐远远落后于流行音乐在商业上的巨大成功,在一些人看来,虽然CD的销量并不代表古典音乐的流行,"古典音乐"一词直到世纪初才出现,试图将从约翰·塞巴斯蒂安·到贝多芬这段时期作为最早指代的黄金时代《牛津英语词典》收录的"古典音乐"是来自于大约许多作家认为"古典"是一个不恰当的名词来形容世纪下半叶以来创作的主流和前卫音乐,因此常用恐吓语录。
 U633687664
U633687664
 U979745175
U979745175