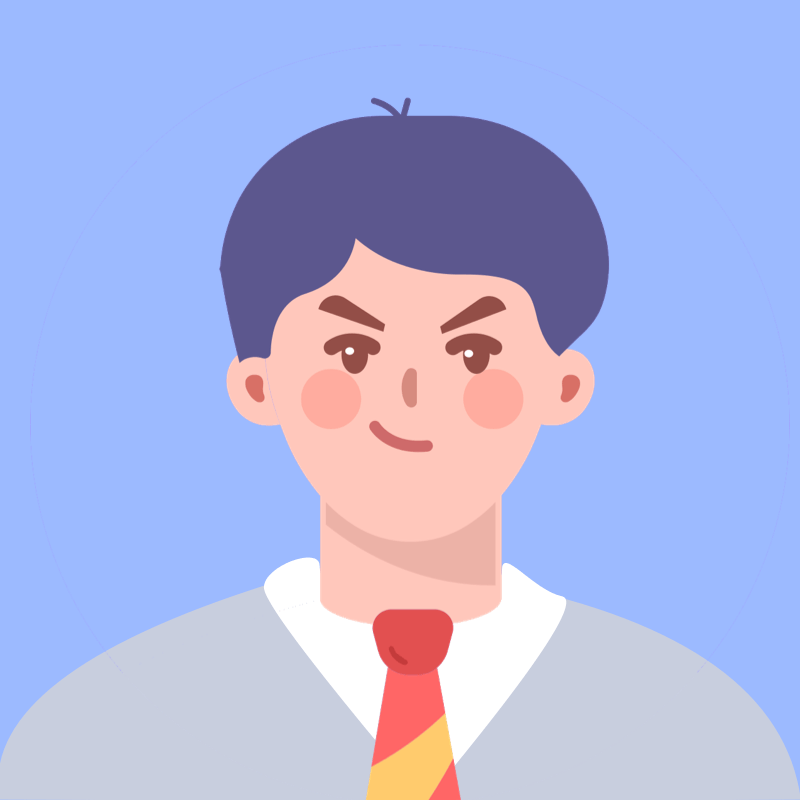
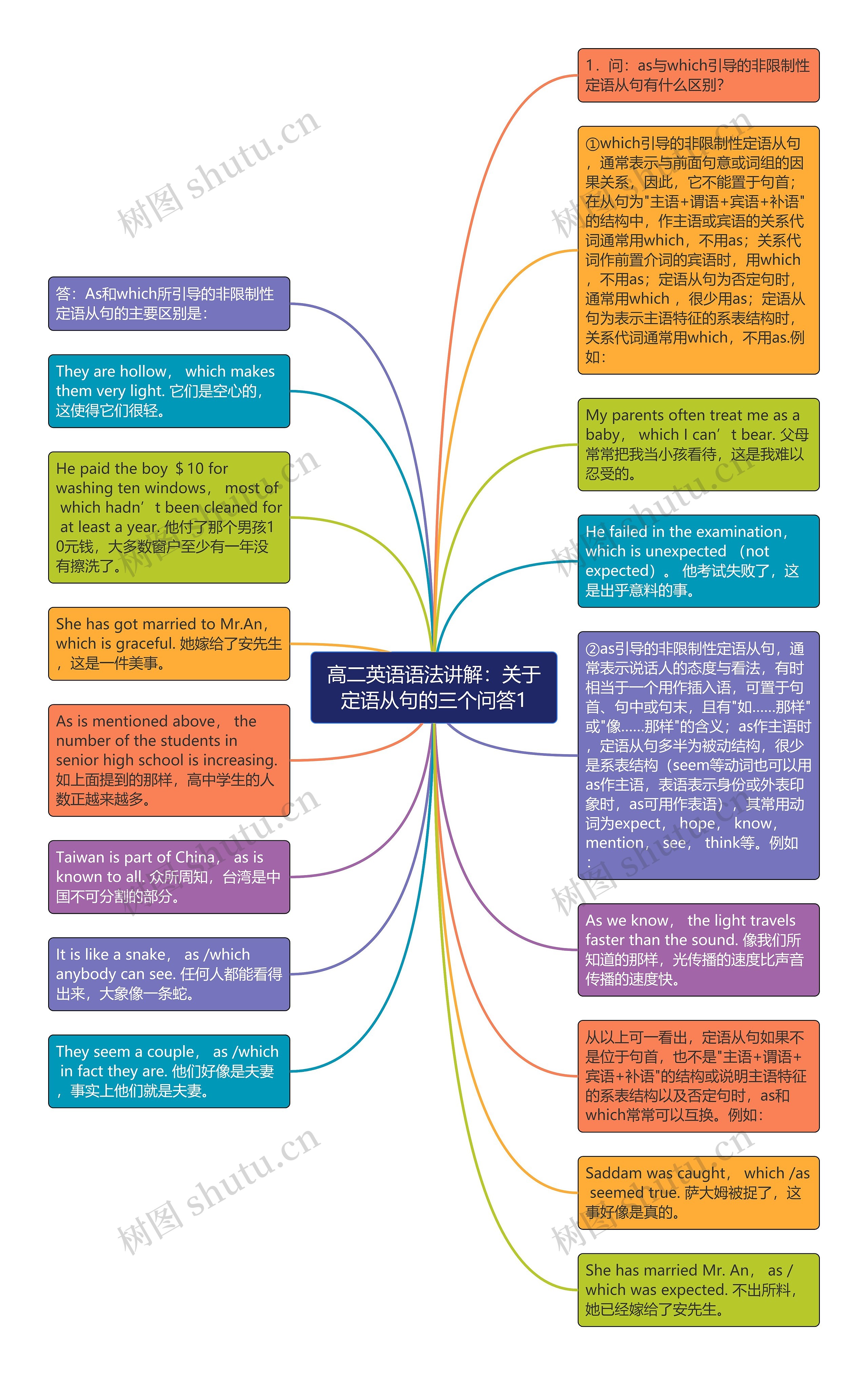
1.问:as与which引导的非限制性定语从句有什么区别?
答:As和which所引导的非限制性定语从句的主要区别是:
①which引导的非限制性定语从句,通常表示与前面句意或词组的因果关系,因此,它不能置于句首;在从句为"主语+谓语+宾语+补语"的结构中,作主语或宾语的关系代词通常用which,不用as;关系代词作前置介词的宾语时,用which,不用as;定语从句为否定句时,通常用which ,很少用as;定语从句为表示主语特征的系表结构时,关系代词通常用which,不用as.例如:
They are hollow, which makes them very light. 它们是空心的,这使得它们很轻。
My parents often treat me as a baby, which I can’t bear. 父母常常把我当小孩看待,这是我难以忍受的。
He paid the boy $10 for washing ten windows, most of which hadn’t been cleaned for at least a year. 他付了那个男孩10元钱,大多数窗户至少有一年没有擦洗了。
He failed in the examination, which is unexpected (not expected)。 他考试失败了,这是出乎意料的事。
She has got married to Mr.An, which is graceful. 她嫁给了安先生,这是一件美事。
②as引导的非限制性定语从句,通常表示说话人的态度与看法,有时相当于一个用作插入语,可置于句首、句中或句末,且有"如……那样"或"像……那样"的含义;as作主语时,定语从句多半为被动结构,很少是系表结构(seem等动词也可以用as作主语,表语表示身份或外表印象时,as可用作表语),其常用动词为expect, hope, know, mention, see, think等。例如:
As is mentioned above, the number of the students in senior high school is increasing. 如上面提到的那样,高中学生的人数正越来越多。
As we know, the light travels faster than the sound. 像我们所知道的那样,光传播的速度比声音传播的速度快。
Taiwan is part of China, as is known to all. 众所周知,台湾是中国不可分割的部分。
从以上可一看出,定语从句如果不是位于句首,也不是"主语+谓语+宾语+补语"的结构或说明主语特征的系表结构以及否定句时,as和which常常可以互换。例如:
It is like a snake, as /which anybody can see. 任何人都能看得出来,大象像一条蛇。
Saddam was caught, which /as seemed true. 萨大姆被捉了,这事好像是真的。
They seem a couple, as /which in fact they are. 他们好像是夫妻,事实上他们就是夫妻。
She has married Mr. An, as /which was expected. 不出所料,她已经嫁给了安先生。
 U633687664
U633687664
 U582679646
U582679646