Chapter 1 introduction思维导图
U431210379
2023-04-08
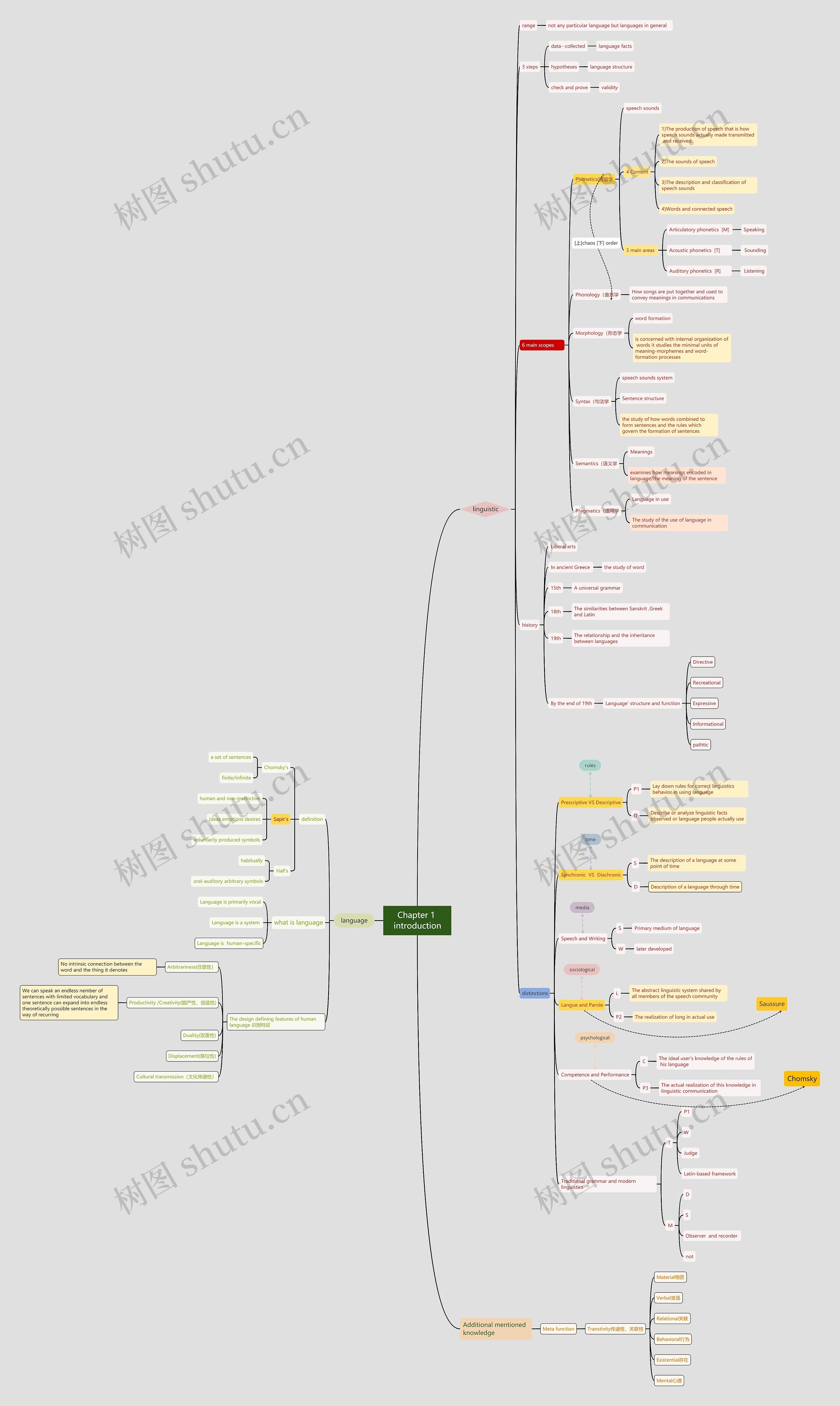
Chapter 1 introduction
树图思维导图提供《Chapter 1 introduction》在线思维导图免费制作,点击“编辑”按钮,可对《Chapter 1 introduction》进行在线思维导图编辑,本思维导图属于思维导图模板主题,文件编号是:c646c3f88c90b2cc3176fd1d31099bbd
思维导图大纲
相关思维导图模版
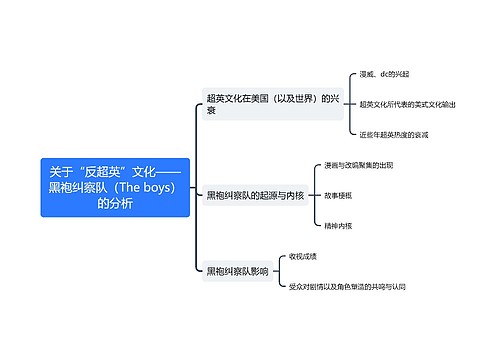
1113爆卡会总结会会议纪要思维导图
 U245265618
U245265618树图思维导图提供《1113爆卡会总结会会议纪要》在线思维导图免费制作,点击“编辑”按钮,可对《1113爆卡会总结会会议纪要》进行在线思维导图编辑,本思维导图属于思维导图模板主题,文件编号是:aaf6c152a765d5821e8e1787f2b3226e
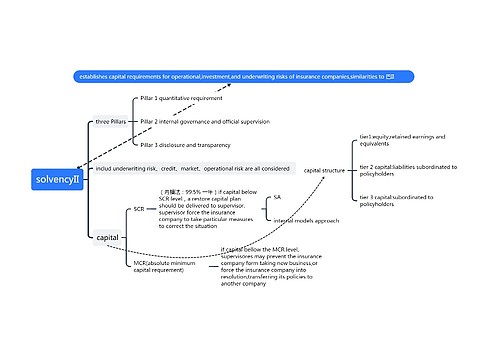
第1章 化工设计基本知识思维导图
 U882667602
U882667602树图思维导图提供《第1章 化工设计基本知识》在线思维导图免费制作,点击“编辑”按钮,可对《第1章 化工设计基本知识》进行在线思维导图编辑,本思维导图属于思维导图模板主题,文件编号是:70ec0519ed26419068a32a511862aadd