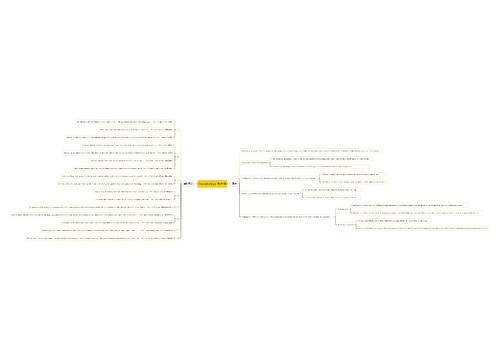
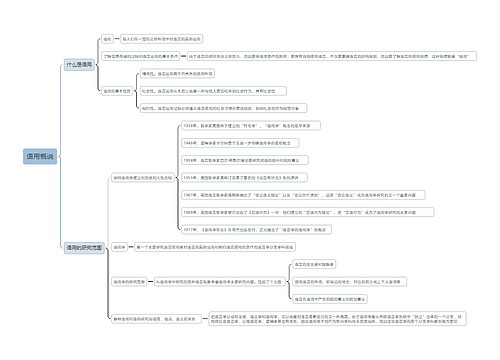
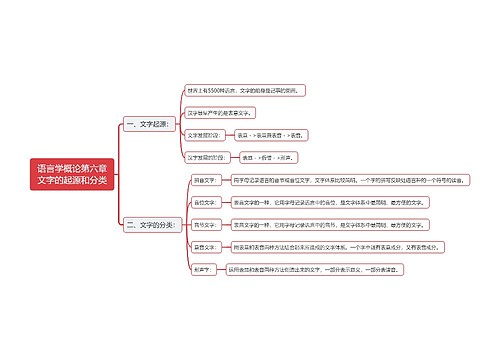
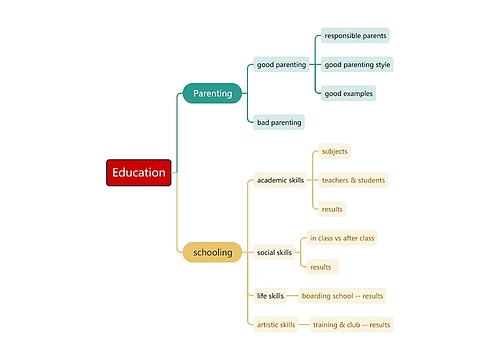
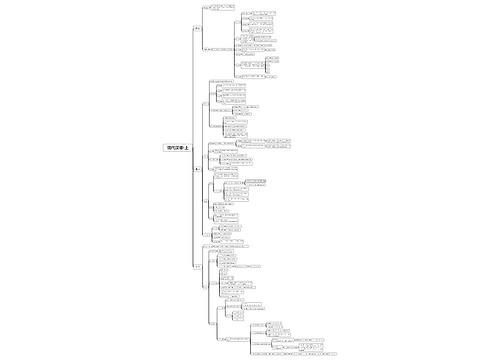
Semantics 语义学思维导图
小周不恰香菜
2022-09-06

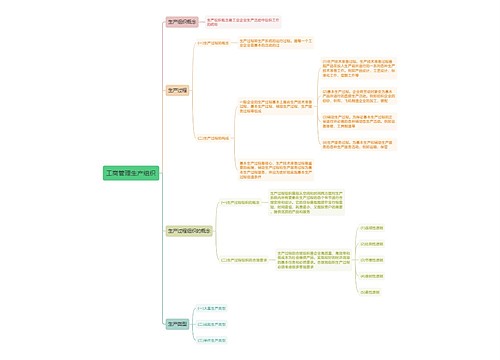
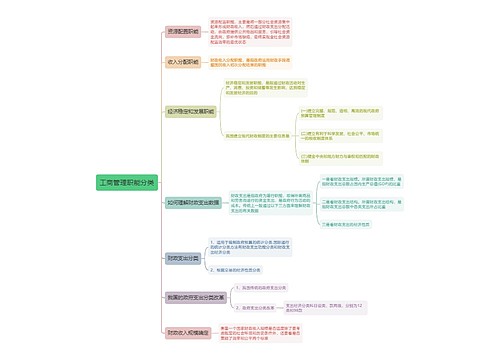
充分了解大学校园教育中关于英语语言学概论的内容(Semantics 语义学),记住关键知识点。
树图思维导图提供《Semantics 语义学思维导图》在线思维导图免费制作,点击“编辑”按钮,可对《Semantics 语义学思维导图》进行在线思维导图编辑,本思维导图属于思维导图模板主题,文件编号是:ed9f1b507769b58aad0cc2d8ecf1a0cd
思维导图大纲
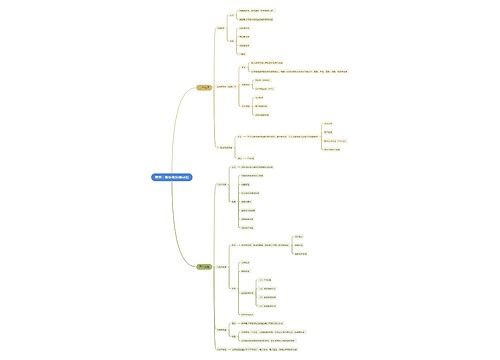
相关思维导图模版
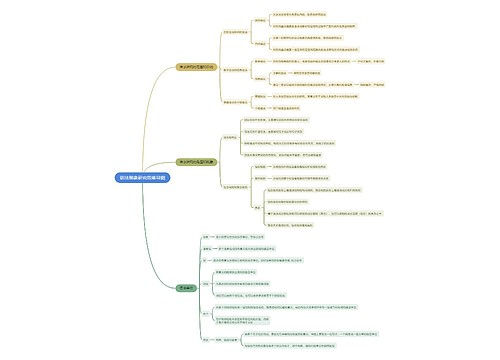
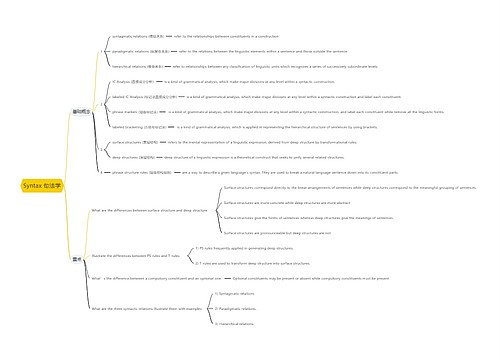
Syntax 句法学思维导图
 小周不恰香菜
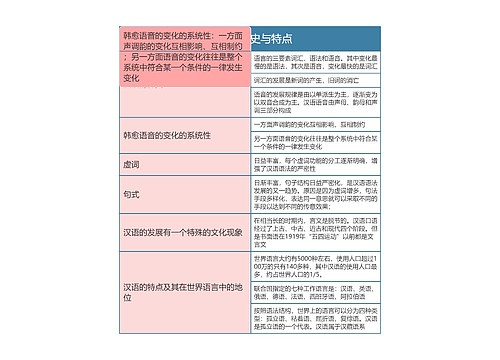
小周不恰香菜树图思维导图提供《Syntax 句法学思维导图》在线思维导图免费制作,点击“编辑”按钮,可对《Syntax 句法学思维导图》进行在线思维导图编辑,本思维导图属于思维导图模板主题,文件编号是:bb6b7b6c94fcebbbca3123f2364e15d9
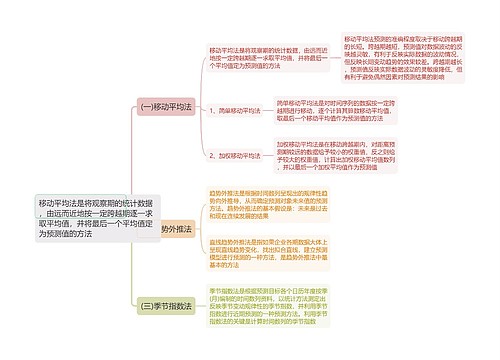
Morphology 形态学思维导图
 小周不恰香菜
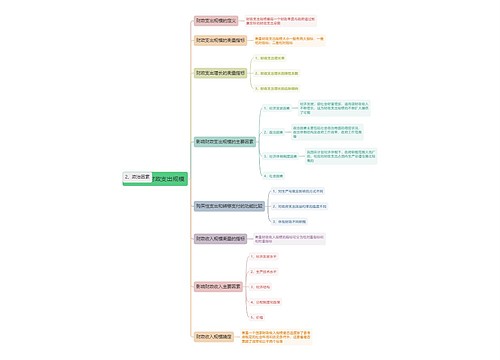
小周不恰香菜树图思维导图提供《Morphology 形态学思维导图》在线思维导图免费制作,点击“编辑”按钮,可对《Morphology 形态学思维导图》进行在线思维导图编辑,本思维导图属于思维导图模板主题,文件编号是:fccf77c98ac737ac1edfd9e99b10e63d