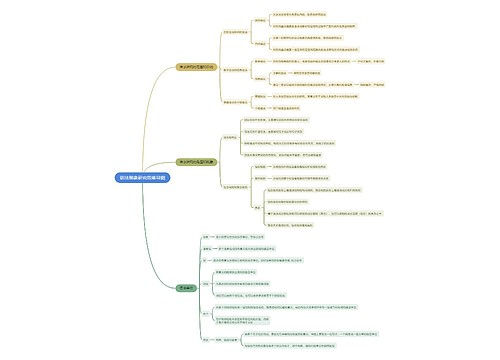
general linguistics and descriptive linguistics (普通语言学与描写语言学)
The former deals with language in general whereas the latter is concerned with one particular language
synchronic linguistics and diachronic linguistics (共时语言学与历时语言学)
Diachronic linguistics traces the historical development of the language and records the changes that have taken place in it between successive points in time.
And synchronic linguistics presents an account of language as it is at some particular point in time.
theoretical linguistics and applied linguistics (理论语言学与应用语言学)
The former copes with languages with a view to establishing a theory of their structures and functions whereas the latter is concerned with the application of the concepts and findings of linguistics to all sorts of practical tasks
microlinguistics and macrolinguistics (微观语言学与宏观语言学)
The former studies only the structure of language system whereas the latter deals with everything that is related to languages.
langue and parole (语言与言语)
The former refers to the abstract linguistics system shared by all the members of a speech community whereas the latter refers to the concrete act of speaking in actual situation by an individual speaker.
competence and performance (语言能力与语言运用)
The former is one’s knowledge of all the linguistic regulation systems whereas the latter is the use of language in concrete situation.
speech and writing (口头语与书面语)
Speech is the spoken form of language whereas writing is written codes, gives language new scope
linguistics behavior potential and actual linguistic behavior (语言行为潜势与实际语言行为)
People actually says on a certain occasion to a certain person is actual linguistics behavior. And each of possible linguistic items that he could have said is linguistic behavior potential
syntagmatic relation and paradigmatic relation (横组合关系与纵聚合关系)
The former describes the horizontal dimension of a language while the latter describes the vertical dimension of a language.
verbal communication and non-verbal communication (言语交际与非言语交际)
Usual use of language as a means of transmitting information is called verbal communication. The ways we convey meaning without using language is called non-verbal communication
 U677263622
U677263622
 U751527064
U751527064