My sister wears glasses. 我妹妹戴眼镜。
He often goes to the cinema. 他经常去看电影。
"Do you ever eat meat?" "No, I never eat meat.""你吃肉吗?""从不吃肉。"
He is always like that. 他总是那样。
He likes living in the country. 他喜欢住在乡下。
We need a lot of money. 我们需要一大笔钱。
Mr. Smith teaches French. 史密斯先生教法语。
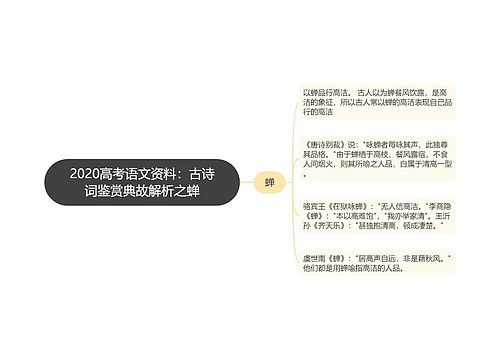
4. 表示客观真理、科学事实、格言以及不受时间限制的客观存在。如:
Summer follows spring. 春去夏来。
Knowledge is power. 知识就是力量。
The earth turns around the sun. 地球绕着太阳转。
1. 当主句为将来时态或表示将来意义时,时间和条件的状语从句必须用一般现在时表将来。如:
I’ll write to her when I have time. 我有空会给她写信。
Turn off the lights before you leave. 走前关灯。
If we hurry, we may catch the bus. 如果赶紧走我们可能赶得上公共汽车。
Tell me in case you get into difficulty. 遇到困难请告诉我。
【注】① 除表示时间和条件的状语从句外,表示让步、相似、比例的从句也必须用一般现在时表示将来。如:
I’ll follow him wherever he goes. 他去哪儿,我就跟着去哪儿。
Whatever you say, I won’t pay. 无论你说什么,我都不会付钱。
Whether we help him or not, he will fail. 无论我们帮他与否,他都会失败。
I’ll have a good time whether I win or lose. 赢也好,输也好,我都将会玩好。
The more you eat, the fatter you will become. 你吃得越多就会越胖。
② 另外,当主句为用将来时态时,定语从句也通常用一般现在时表将来。如:
I’ll give you anything you ask for. 你要什么我都给你。
You can have anything I find. 我找到的任何东西你都可以拿去。
Everyone who comes first will get a present. 每个先来的人都可得到一份礼物。
2. 按照英语习惯,一个句子中若主要动词已经表明了所谈论动作的时间,那么与之相关的其他动词就不必再次指明同一时间,而往往使用一个比较简单的时态,如用一般现在时表示一般将来时等。比较。如:
This discovery means that we will spend less on food.这一发现意味着我们将减少在食品上的花费。
This discovery will mean that we spend less on food. 这一发现意味着我们将减少在食品上的花费。
3. 在make sure(弄清楚),make certain(弄清楚),take care(注意,当心),be careful(注意,当心),mind(注意),watch(注意)等后的that从句中通常也只用一般现在时表示将来意义。如:
Take care that it does not occur again. 注意别再发生这样的事。
We must take care that no one sees us. 我们必须注意别让人看见我们。
Make sure you come back soon. 你要保证快点回来。
Be careful that you don’t hurt her feelings. 当心别伤了她的感情。
Watch that the baby doesn’t go near the heater. 注意别让宝宝接近加热器。
Mind you read the examination questions carefully before you begin to answer them. 在答题前要注意仔细阅读考题。

 U245265618
U245265618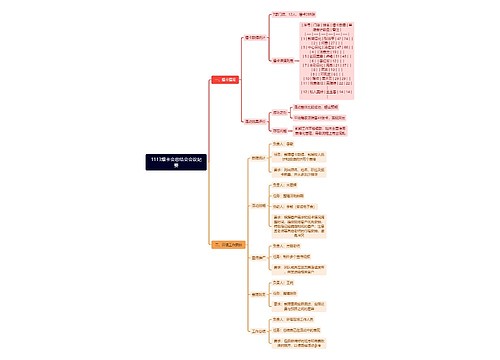
 U882667602
U882667602